Company name: Ansteel Machinery Development Private Enterprise Machinery Factory
Anshan Shuangxing Galvanizing Co., Ltd
Contact: Shen Taisheng
WhatsApp:+8615382137795
Tel.: 0412-8812449
Q Q:1481198998
Postal code: 114000
Email: bestgalvanizing@163.com
Website: www.agxinguo.com
Plant site: Ansteel plant
Office address: No. 111, Ximinsheng Road, Tiexi District, Anshan, Liaoning
1. Storage of zinc pot
The surface of the corroded or rusted zinc pot will become quite rough, which will cause more serious corrosion of liquid zinc. Therefore, if the new zinc pot needs to be stored for a long period of time before use, anti-corrosion protection measures should be taken, including painting protection, putting it in the workshop or covering to avoid rain, padding the bottom to avoid soaking in water, etc. Under no circumstances should water vapor or water accumulate on the zinc pot.
2. Installation of zinc pot
When installing the zinc pot, it must be moved into the zinc furnace according to the requirements of the manufacturer. Before using a new boiler, be sure to remove the rust, residual welding slag spatter and other dirt and corrosives on the boiler wall. Rust shall be removed by mechanical method, but the surface of the zinc pot shall not be damaged or rough. A hard synthetic fiber brush can be used for cleaning.
The zinc pot will expand when heated, so there should be room for free expansion. In addition, when the zinc pot is in high temperature for a long time, "creep" will occur. Therefore, proper supporting structure shall be adopted for the zinc pot during design to prevent it from gradually deforming during use.
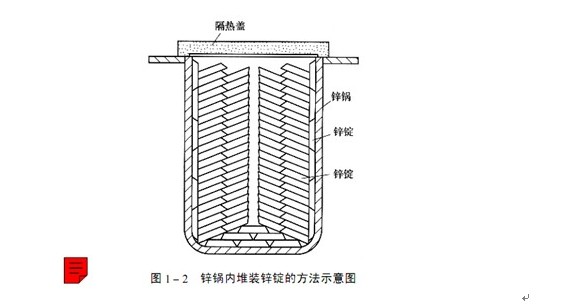
3. Stacking of zinc ingots in zinc pot
When loading zinc ingots into the new zinc pot, zinc ingots with good quality must be selected to reduce the harmful effect of liquid metal on the zinc pot. When the zinc ingots are loaded into the zinc pot, they should be placed according to the method shown in Figure 1-2 to ensure good heat conduction between the zinc ingots and the pot wall. The zinc ingot can be covered with a layer of charcoal, which can not only play the role of thermal insulation, but also play the role of preventing zinc oxidation; The zinc pot can also be covered with an insulating cover to reduce heat loss. Since the thermal expansion coefficient of zinc is three times that of iron, in order to prevent the expansion of zinc from exerting too much pressure on the pot wall during heating and temperature rise, when placing zinc ingots, sufficient clearance should be left in the middle of the length direction of the zinc pot, and some wooden strips can be placed in the middle of this clearance. During the heating of the zinc pot, these sticks will be squeezed by the expanded zinc ingots, and then burned. The unburned sticks and combustion products will finally float to the surface of the zinc liquid.
During the heating process, the zinc ingot near the pot wall first melts, and the molten zinc reacts with the pot wall to form a protective layer of iron zinc alloy.
4. Temperature rise and zinc melting
Before the zinc ingot is melted and reaches the working temperature, the zinc pot is in danger of cracking and damage due to the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the zinc pot wall and the corrosion of liquid metal.
The tensile strength of steel decreases with the increase of temperature. At 450 ℃, the tensile strength is less than 100MPa. The temperature difference between the inside and outside of the zinc pot wall will produce tensile stress on the inside of the pot wall. For example, when the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the zinc pot wall reaches 60 ℃, a tensile stress of 120~130MPa will be generated on the pot wall, which is higher than the tensile strength of steel. The hydrostatic pressure of zinc liquid on the boiler wall will also cause tensile stress on the boiler wall. The maximum tensile stress value generated by the superposition of the tensile stress generated by these two reasons appears in the turning area between the vertical wall and the bottom of the zinc pot, especially in the middle of the long side of the zinc pot, so this part is the most dangerous area during the heating process. In order to avoid cracking and damage of zinc and aluminum, heating and cooling must be very slow, so as to minimize the temperature difference of various parts of the zinc pot.
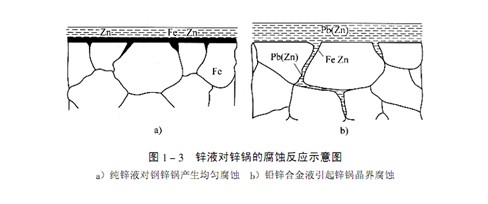
Normally, a layer of iron zinc alloy will be uniformly formed on the inner surface of the zinc pot when the pure zinc liquid reacts with the zinc pot, as shown in Fig. 1-3a. If lead is added when the zinc ingot is loaded in a new zinc pot, the liquid lead layer containing unsaturated zinc has accumulated at the bottom of the zinc pot before the protective iron zinc alloy layer is formed during the zinc melting process. The liquid lead layer containing unsaturated zinc contacts the steel plate of the zinc pot, which will cause intergranular damage to the steel plate of the zinc pot, as shown in Figure 1-3b. Due to stress concentration, intergranular damage occurs at the turning point between the side and bottom of the zinc pot, which is particularly dangerous.
When the zinc pot is used in the critical temperature range, the corrosion rate of liquid zinc will be greatly increased and the zinc pot will be damaged prematurely. If there are four pits on the zinc pot wall and the temperature at the thinner pot wall is higher, the corrosion rate of zinc on the zinc pot will increase. If the zinc pot wall is heated unevenly, the corrosion rate of zinc liquid on the pot wall will be accelerated in the area with high heating temperature.
The new zinc pot must be heated slowly and evenly according to the requirements of the zinc pot manufacturer.
Although this will significantly increase the cost of heating and equipment operation, it is much lower than the loss caused by zinc pot damage and production stoppage. In the process of heating, it is important to maintain a certain temperature balance throughout the zinc pot, that is, the temperature of the inner wall of the zinc pot must be lower than 480 ℃, the temperature difference between the pot wall and the pot bottom must be less than 11 ℃, and the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the pot wall must be less than 50 ℃.
The heating time required for heating and melting zinc depends on the size and geometry of the zinc pot. In order to maintain a certain temperature balance, the heating time of melting zinc in a larger zinc pot is relatively long. The heating curve of a zinc pot is shown in Fig. 1-4. Before the inner wall of the zinc pot is heated to 300 ℃, the temperature should rise slowly; When reaching 300 ℃, keep it for a period of time, so that it will not pose a danger to the zinc pot; The final temperature rise stage above 300 ℃ can be faster, but it must be noted that the above critical temperature difference cannot be exceeded.
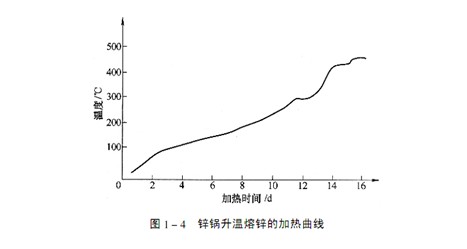
For the zinc plating furnace with brick furnace body (or part of the furnace body is brick), the brick body must be dried slowly before the zinc pot is used, and then the heating and zinc melting shall be carried out according to the curve shown in Fig. 1-4.
In order to make the temperature measurement and control accurate, the temperature measurement points should be correctly selected and the perfect temperature measurement and control system should be configured. The outer wall and bottom of the zinc pot are selected as the temperature measuring points of the thermocouple, and the temperature difference between the pot wall and bottom (the hottest and coldest parts) can be easily controlled within 100 ℃ by using appropriate control equipment.